Antibodies are essential for immune defense and safeguarding against bacteria, viruses, and other foreign entities. Produced by B cells, these protein molecules offer the potential for treating cancers, autoimmune disorders, and infectious diseases.
However, modified therapeutic antibodies can see a reduction in efficacy as the human immune system recognizes them as foreign substances. Two techniques have been devised to overcome this obstacle: antibody humanization and affinity maturation.
The biotech industry has experienced a revolution in the last 10-20 years due to advancements in antibody humanization and affinity maturation. These techniques have enabled the development of exceptionally potent therapeutic antibodies with a broad spectrum of applications in treating various diseases.
Before antibody humanization and affinity maturation, therapeutic antibody development was slow and challenging. It relied on less effective non-human sources, leading to unwanted immune responses and low binding affinities.
Antibody humanization and affinity maturation have transformed this paradigm by facilitating the development of highly effective therapeutic antibodies for disease treatment.
By enhancing binding to target molecules, prolonging half-lives within the body, and enhancing immune cell recruitment, these processes have effectively improved the efficacy of therapeutic antibodies, all while mitigating the risk of immune response activation in humans.
Hence, the progress in antibody humanization and affinity maturation technology has enormous potential to facilitate the development of enhanced therapeutic antibodies.
Antibody humanization
The process of antibody humanization plays a pivotal role in the development of therapeutic antibodies. It involves the modification of non-human antibody molecules to enhance their compatibility with the human immune system.
While non-human antibodies, such as those derived from mice and rabbits, are frequently utilized in research for therapeutic antibody development, their use as therapeutic agents in humans can lead to an immune response, thereby diminishing their effectiveness.
Humanization has altered the order of amino acids in a non-human antibody molecule to match that of a human antibody molecule.
X-Ray crystallography and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy are used to determine the antigen-binding site. Following that, bioinformatics and computer modeling tools are employed to forecast the structural consequences of changes to the framework and complementarity-determining region (CDR).
By undergoing this process, a molecule is generated that can serve as a highly effective therapeutic agent in humans without triggering an immune response.
In conclusion, antibody humanization plays a crucial role in the development of therapeutic antibodies by reducing their immunogenicity and enhancing their efficacy in treating diseases when used in humans. (Figure 1)
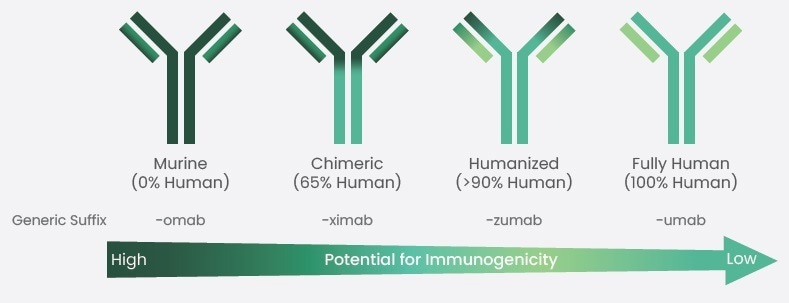
Figure 1. Humanization of therapeutic antibodies has reduced their immunogenicity. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Sino Biological provides an antibody humanization service utilizing its CDR grafting technology, which boasts a remarkable success rate of 100% and achieves over 95% sequence homology with human antibody frameworks.
The company’s humanized antibody packages guarantee equal or even higher affinity when compared to any parental or chimeric antibody. (Figure 2)

Figure 2. Complementarity-determining region (CDR) grafting technology developed by Sino Biological. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Affinity maturation
Affinity maturation is an essential process in the development of exceptionally potent therapeutic antibodies.
The process entails the introduction of mutations in the CDRs of an antibody, leading to structural alterations that enhance its ability to interact optimally with the antigen. This process effectively increases the binding affinity, i.e., the strength of the interaction between the antibody and its target.
A higher affinity signifies the antibody’s increased effectiveness in binding to its target and eliciting a response. Traditionally, affinity maturation has involved iterative rounds of testing and modification to identify an amino acid sequence that optimizes the antibody’s affinity toward the target.
Application of artificial intelligence
The application of artificial intelligence (AI) has brought about a significant transformation in the field of antibody humanization and affinity maturation within the biotech industry.
AI can recognize specific amino acid sequences that are highly likely to augment the binding affinity between the antibody and its target while also ensuring compatibility with the human immune system through the analysis of large datasets containing antibody molecules.
This has drastically reduced the time and expense involved with therapeutic antibody creation, making the procedure more accessible to researchers and biotech firms.
As a result, there has been an increase in the development of therapeutic antibodies and a notable reduction in the time required for these antibodies to reach the market.
Sino Biological has partnered with Ainnocence to offer advanced AI-based antibody affinity maturation and de novo design. Utilizing Ainnocence’s SentinusAITM AI search engine, this platform effectively ranks up to 1010 antibody sequences based on predicted affinity to antigens.
Sino Biological offers a high-throughput recombinant antibody development service that can produce >1000 high-purity antibodies per project. SentinusAITM is used to validate the affinities of these antibodies.
Real-World applications of antibody humanization and affinity maturation
The biotech industry has witnessed a notable transformation through antibody humanization and affinity maturation, specifically in the realm of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) developed for cancer treatment.
These mAbs are specifically engineered to bind to particular molecules found on cancer cells, stimulating an immune response that destroys these cells.
Humanization and affinity maturation have aided in the creation of mAbs with improved properties such as reduced immunogenicity, high specificity, and therapeutic efficacy.
Humanization and maturation of antibodies have also had an impact on the production of therapeutic antibodies for the treatment of autoimmune disorders, including rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis, which are caused by the immune system attacking the body’s tissues.
Humanized and affinity-matured antibodies have enabled the creation of very effective medicines capable of suppressing the immune response responsible for autoimmune disorders.
The humanization and affinity maturation of antibodies has also been instrumental in developing highly effective vaccines, protecting a diverse array of infectious diseases, including viral infections such as HIV, hepatitis C, and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
Apart from their significant role in therapy and vaccine development, antibody humanization and affinity maturation have created novel prospects for biotech companies and researchers.
These processes have facilitated the reduction of immunogenicity and the enhancement of specificity, paving the way for the exploration and development of innovative therapies and treatments.
Conclusion
Antibody humanization and affinity maturation have revolutionized the biotech industry by enabling highly effective therapeutic antibodies, vaccines, and treatments in the past two decades.
The integration of AI in these processes has expedited their development, enhancing accessibility for biotech companies and researchers.
As these technologies advance further, their potential impact on the biotech industry is poised to expand significantly, facilitating the creation of novel and groundbreaking therapies targeting a diverse array of diseases.
Both antibody humanization and affinity maturation play vital roles in the development of therapeutic antibodies.
Nevertheless, conventional approaches linked to these processes can be laborious and costly. AI has revolutionized these processes, reducing time and costs by analyzing massive antibody datasets to identify optimal amino acid sequences for humanization and affinity maturation.
The data can be utilized to modify the antibody molecule, leading to the creation of a more potent therapeutic agent. While the implementation of AI in antibody humanization and affinity maturation is still in its nascent phase, the potential advantages of this technology are evident.
Advancements in AI algorithms will enable the analysis of larger datasets, resulting in more accurate predictions. This progress will further decrease the time and costs associated with antibody humanization and affinity maturation.
AI is set to become a vital tool in therapeutic antibody development because it can optimize antibody sequences and structures, identify new targets, assist in repurposing existing drugs and antibodies, and conduct high-throughput screening.
About Sino Biological Inc.

Sino Biological is an international reagent supplier and service provider. The company specializes in recombinant protein production and antibody development. All of Sino Biological's products are independently developed and produced, including recombinant proteins, antibodies, and cDNA clones. Sino Biological is the researchers' one-stop technical services shop for the advanced technology platforms they need to make advancements. In addition, Sino Biological offers pharmaceutical companies and biotechnology firms pre-clinical production technology services for hundreds of monoclonal antibody drug candidates.
Sino Biological's core business
Sino Biological is committed to providing high-quality recombinant protein and antibody reagents and to being a one-stop technical services shop for life science researchers around the world. All of our products are independently developed and produced. In addition, we offer pharmaceutical companies and biotechnology firms pre-clinical production technology services for hundreds of monoclonal antibody drug candidates. Our product quality control indicators meet rigorous requirements for clinical use samples. It takes only a few weeks for us to produce 1 to 30 grams of purified monoclonal antibody from gene sequencing.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.